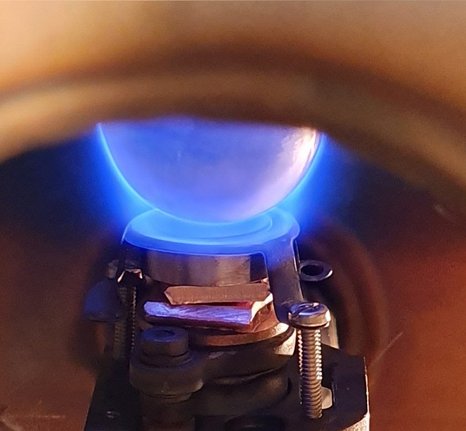
Dielectric Barrier Discharge - DBE
Dielectric barrier discharges (DBD) are low-temperature plasmas that can be used for surface functionalization, coating and material removal. DBE plasmas are characterized, among other things, by a low gas temperature which is usually only a few degrees above room temperature. As DBE plasmas can be ignited under atmospheric pressure, they are used in many areas. For example, dielectrically impeded discharges can be used to functionalize plastic surfaces for better adhesion to metal materials, treat skin diseases and wounds, deposit semiconducting and insulating thin films and remove impurities from surfaces and gases.
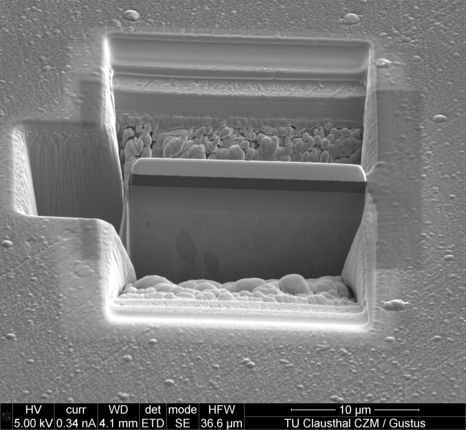
Focused Ion Beam - FIB
The FIB technique can be used to make defined incisions in sample surfaces. The preparation technique is mainly used in scanning electron microscopes. The incisions are created using gallium ions, which are focused using ion optics and accelerated onto the surface. Similar to SEM, the gallium ion beam is moved across the surface in a grid pattern. The transfer of energy and momentum causes material to be removed from the surface. The FIB technique is mainly used for depth profile analysis. For this purpose, a step-shaped incision is usually made in the surface and the cut edge is examined using SEM/EDX. In this way, for example, the elemental composition can be analyzed as a function of depth. FIB can also be used to prepare thin lamellae (100-300 nm) from the surface, which can be used for STEM and TEM examinations.
Physical vapor deposition - PVD
Physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a coating process that can be used to deposit thin layers (a few nm to several µm) of a material on any material surface. The layers are usually prepared under vacuum conditions, whereby the material is first converted into the gas phase, for example by heating or ion bombardment, and then deposited on the substrate surface by condensation. Almost all materials from metals to organic molecules can be deposited using PVD. In surface physics, PVD technology is used, among other things, to investigate the physical-chemical interaction between atoms or molecules and material surfaces.
UHV preparation
Further preparative techniques are available in the various vacuum apparatuses for the investigation of physical-chemical interactions and reactions on surfaces.
Annealing: Using electron impact heating, samples can be heated up to approx. 1500°C in a vacuum.
Ar-ion sputtering: A material removal method that can be used to remove surface contamination from sample surfaces and to carry out depth profile analyses.
Gas supply: Gas injection systems can be used to inject defined gases into the vacuum chamber. This makes it possible, for example, to investigate the interaction of certain gases with material surfaces.